In today’s digital age, where we spend most of our time sitting in front of screens, learning how to stand up straight has become essential for maintaining good health. Poor posture can lead to chronic pain, anxiety, and musculoskeletal issues. On the flip side, standing up straight brings numerous benefits, including increased confidence, better breathing, and more energy. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how to stand up straight by incorporating practical exercises and routines into your daily life.
1. Why Is Standing Up Straight Important?
Before diving into how to stand up straight, it’s crucial to understand the significance of maintaining proper posture. Good posture helps your body align correctly, reducing the strain on your muscles and ligaments when you move or lift. Without it, you may suffer from::
- Chronic back pain
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Joint Deterioration.
Practicing proper posture not only helps to avoid these issues, but it also enhances your physical look and confidence.
2. The Benefits of Standing Straight
- Supports Musculoskeletal Wellness: Proper alignment relieves tension on muscles and joints, lowering the likelihood of injury.
- Improves Lung Functions: Standing straight allows the lungs to expand without restriction, which leads to increased oxygen intake and more energy.
- Enhances Circulation: Correct posture promotes blood flow, which is critical to general health and dynamism.
- Increases Confidence: The way a person positions their body can influence both their own and other people’s views. Standing up straight demonstrates confidence and aggressiveness.
3. How to Check Your Posture
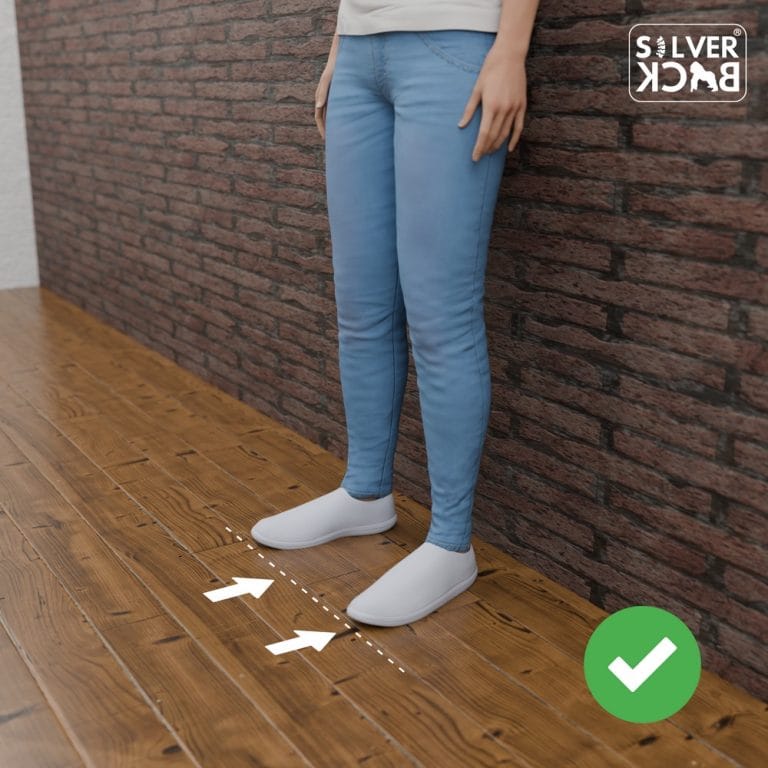
Step 1: Wall Test.
To get started, we will employ a basic yet efficient procedure known as the Wall Test. This practice provides rapid feedback on your present posture and acts as a benchmark for development.
Steps and Directions:
A. Locate a Flat Wall:
Locate an empty wall in the house or business that is easy to stand against.
B. Place Yourself:
Stand with your back against the wall, making sure the following regions are in contact:
- Head – Upper back.
- Lower back (tailbone).
- Heels.
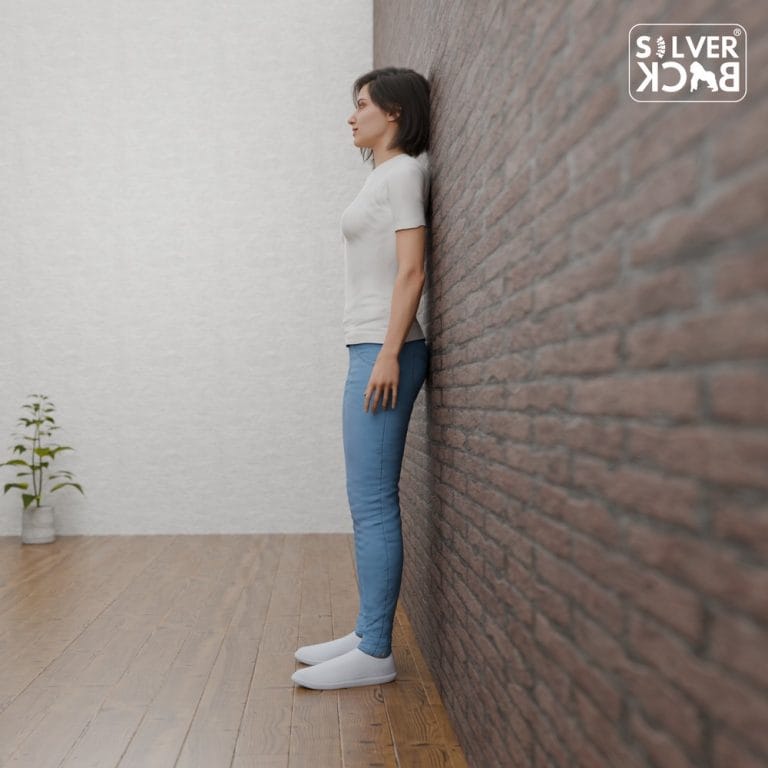

C. Pay attention to the Points of contact:
– Determine which body parts makes touch with the wall. A large space between your lower back and the wall suggests severe bending (hyperlordosis).
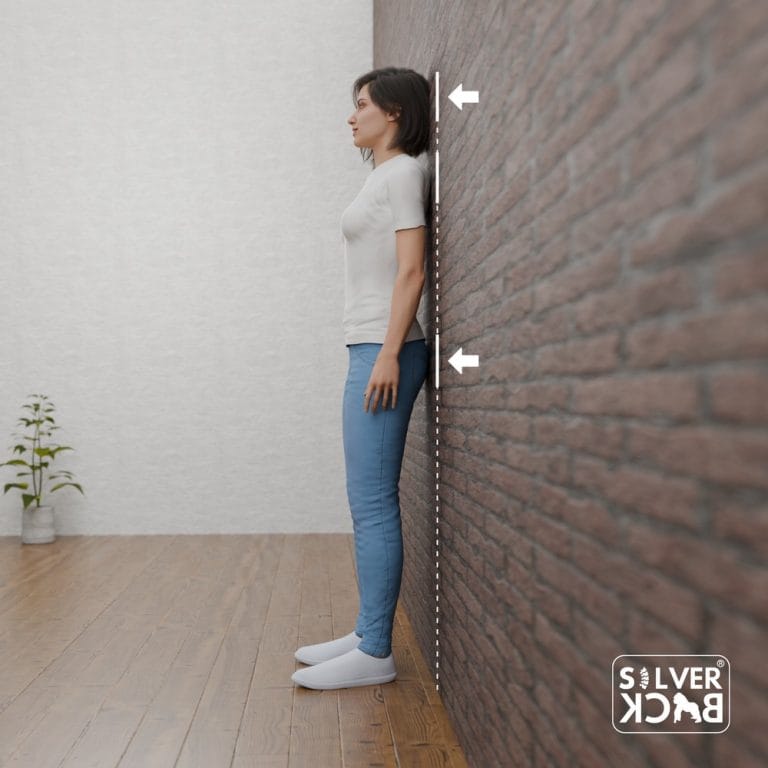

D. Move Away:
Carefully move away from the wall while remaining in this position.
E. Hold Your Position:
Stand straight in your new position. Your ears must be aligned with your shoulders, which must be relaxed and back.
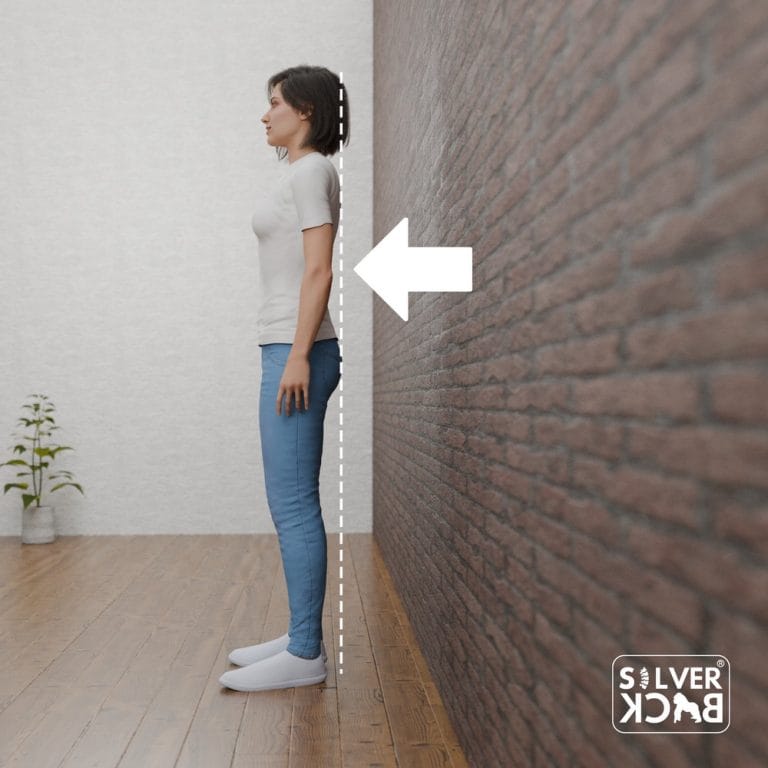

Step 2: How to Stand Up Straight: Key Posture Checkpoints
After performing the Wall Test, it’s important to remember certain checkpoints to maintain how to stand up straight throughout the day:
A. Head Position:
Keep your chin level, not inclined up high or tucked in. Imagine a cord dragging the top of your head higher.

B. Spine Alignment:
Your spine should retain its original curvature. This indicates a little inward bend in the lower back and a little outwards curve in the upper back.
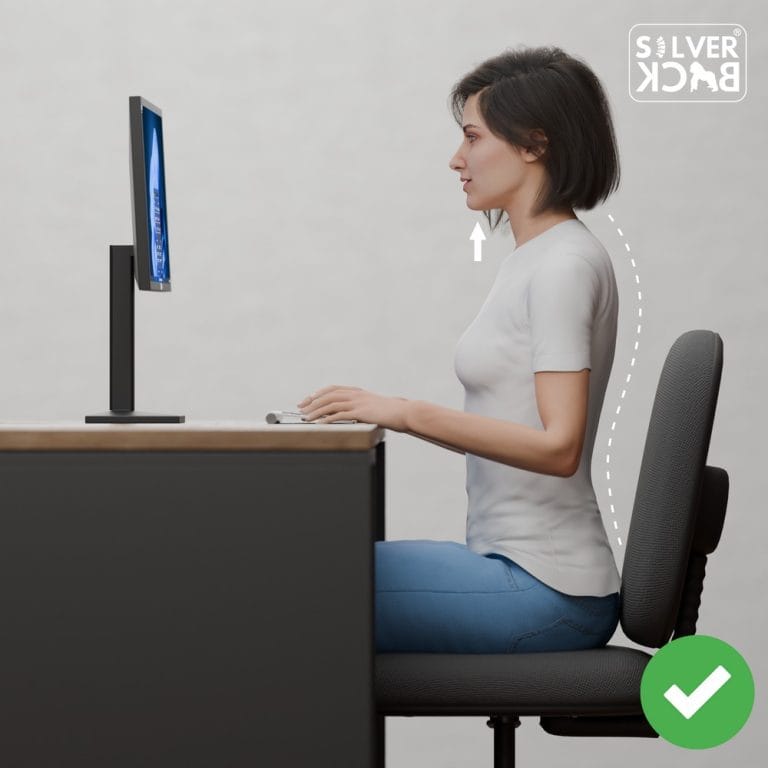

C. Shoulder Alignment:
Your arms and shoulders should be back and relaxed, far from your ears. Avoid sagging or curving.
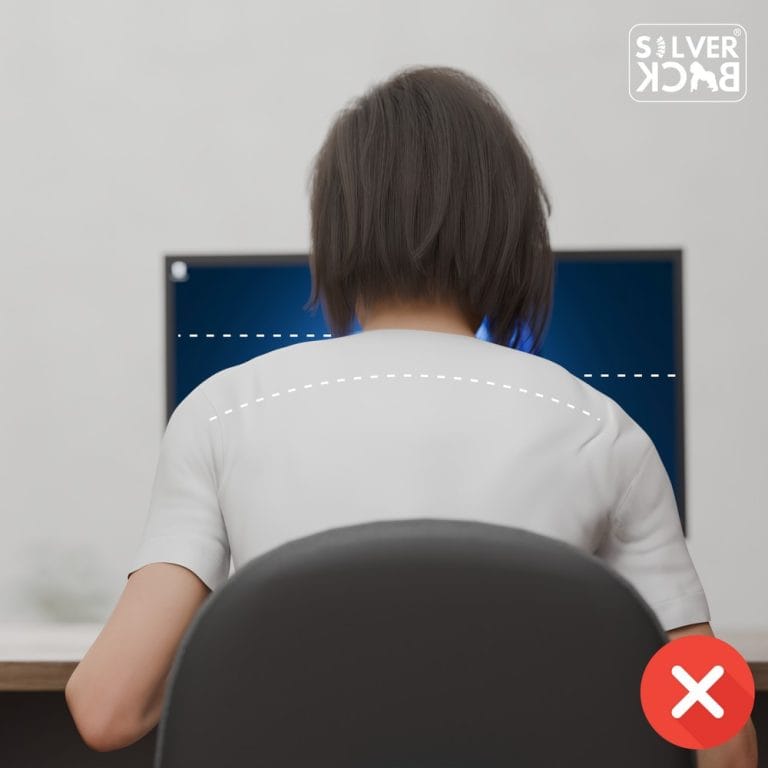
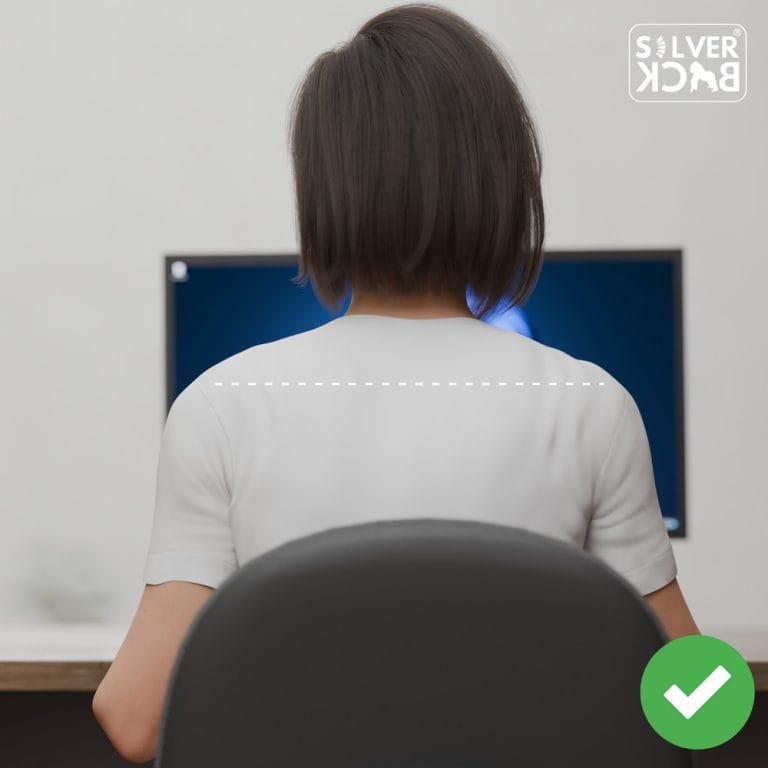


D. Hip Positioning:
Spread your weight equally over both feet, maintaining your hips level and in line with your lower extremities.


4. Effective Exercises to Help You Stand Up Straight
Developing core muscles and increasing flexibility are critical: For correcting posture: To treat particular posture concerns, a variety of exercises are capable of being performed at home, at work, or in the gym.
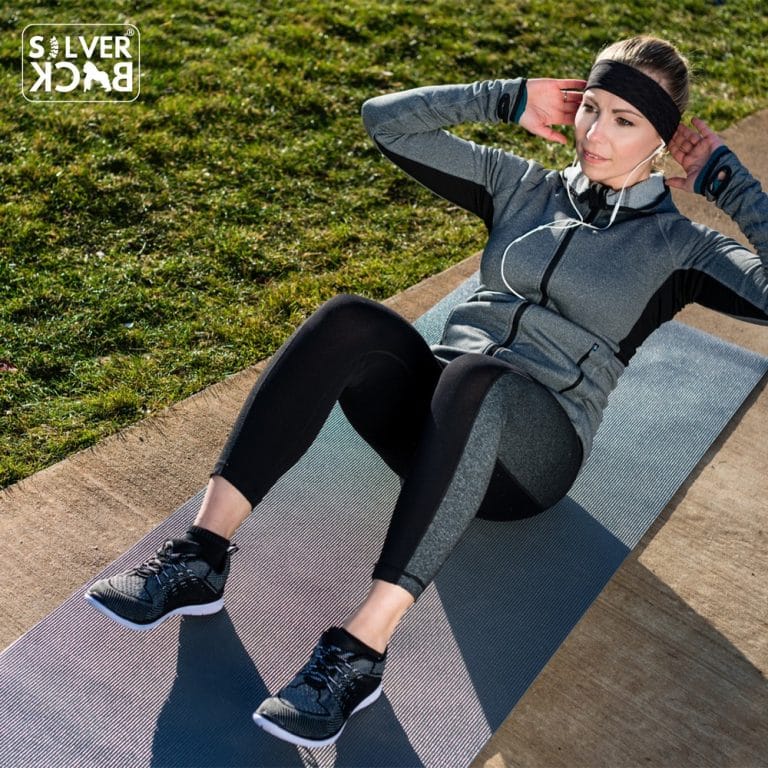
- Partial crunches: improve core and back muscles, enhancing posture and reducing back pain.

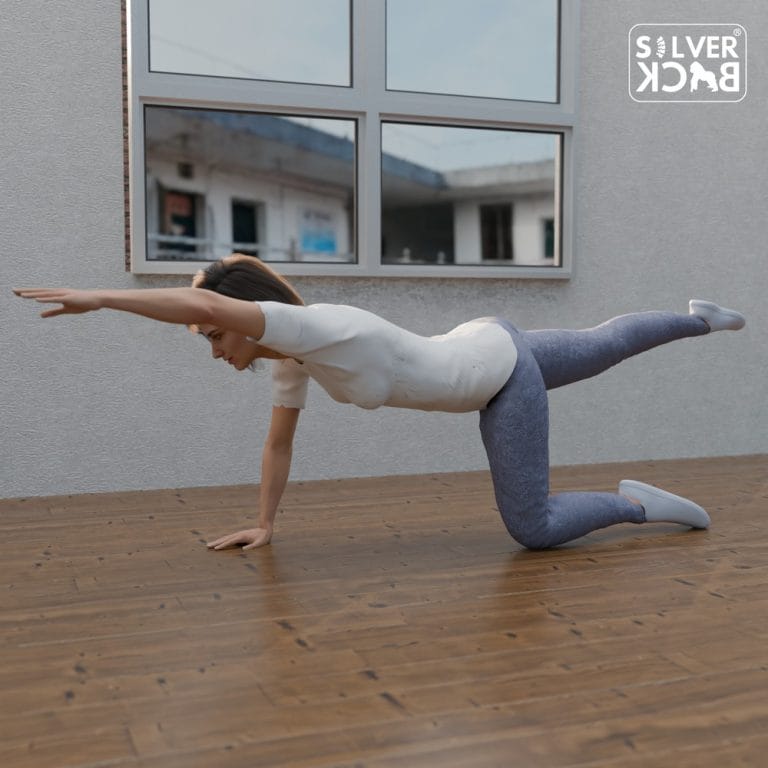
- The bird dog exercise: helps stabilise the core and lower back muscles throughout arm and leg motions.

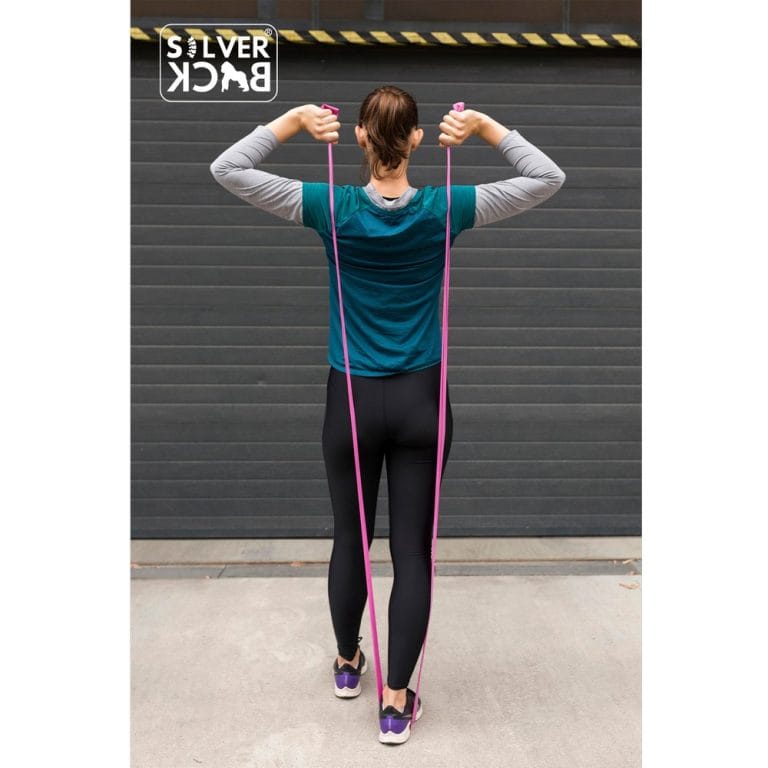
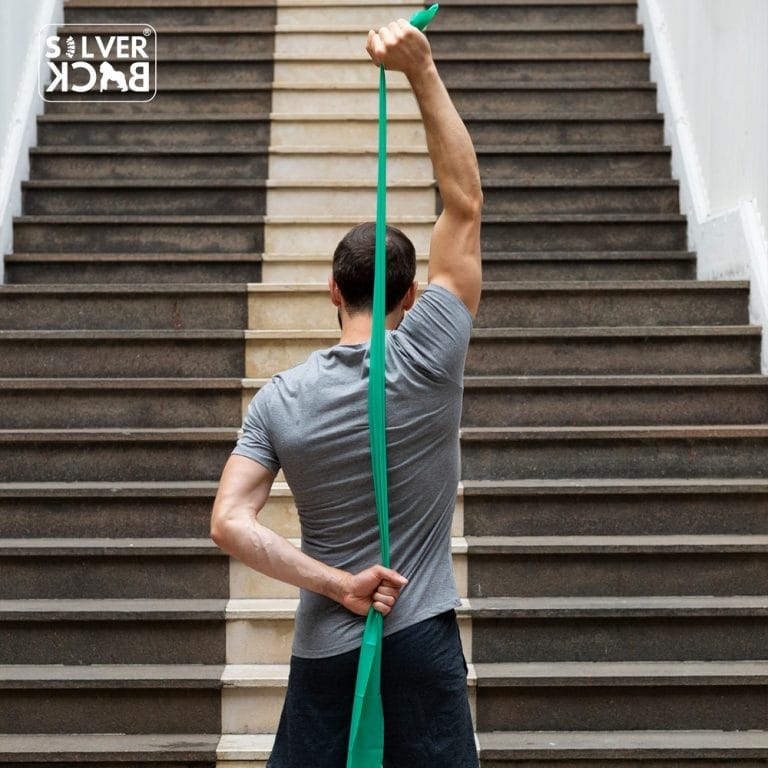
- Standing shoulder presses: can avoid slouching and neck pain for office workers.


- Wall sits: improve posture, strengthen leg muscles, and provide a refreshing respite from sitting.
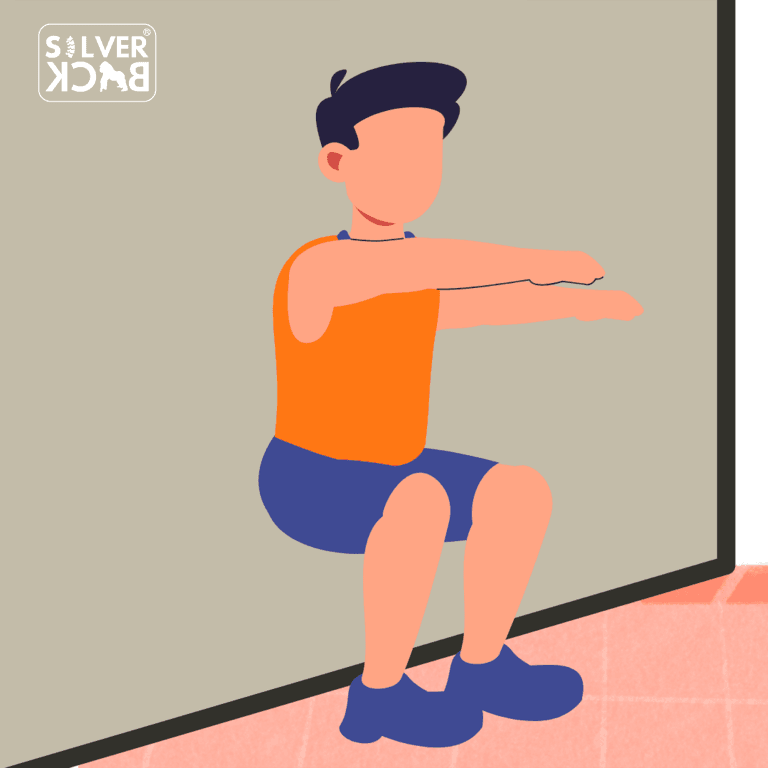
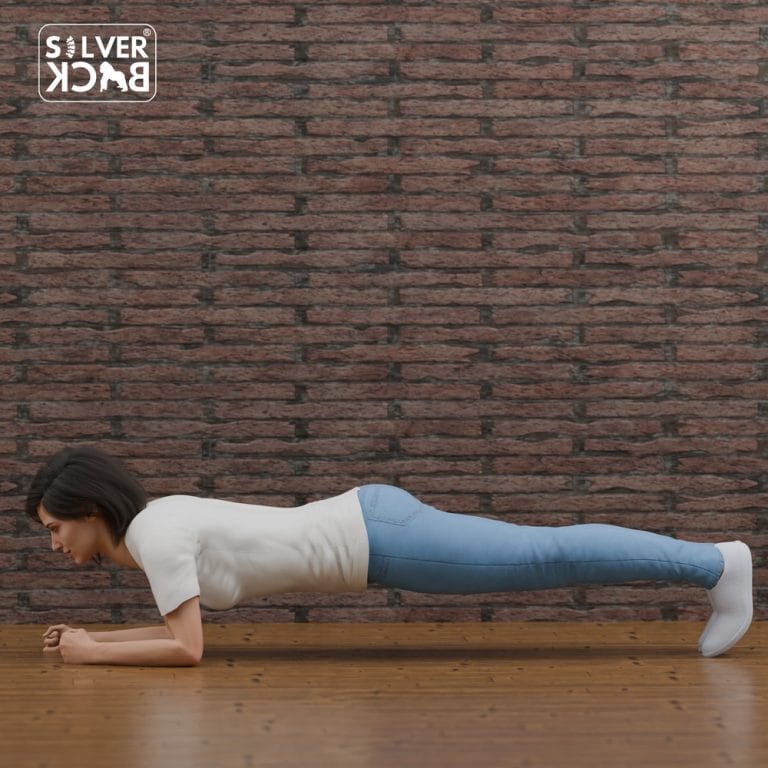
- Planks: strengthen all parts of the body, reducing back discomfort and improving posture.

5. How to Stand Up Straight: Awareness and Commitment.
Awareness is the foundation of proper posture. Here are a few ways to incorporate this awareness into your everyday routine:
A. Mindfulness Reminders:
Use sticky notes, alarms or phone notifications to remind yourself of checking your posture during your entire day.
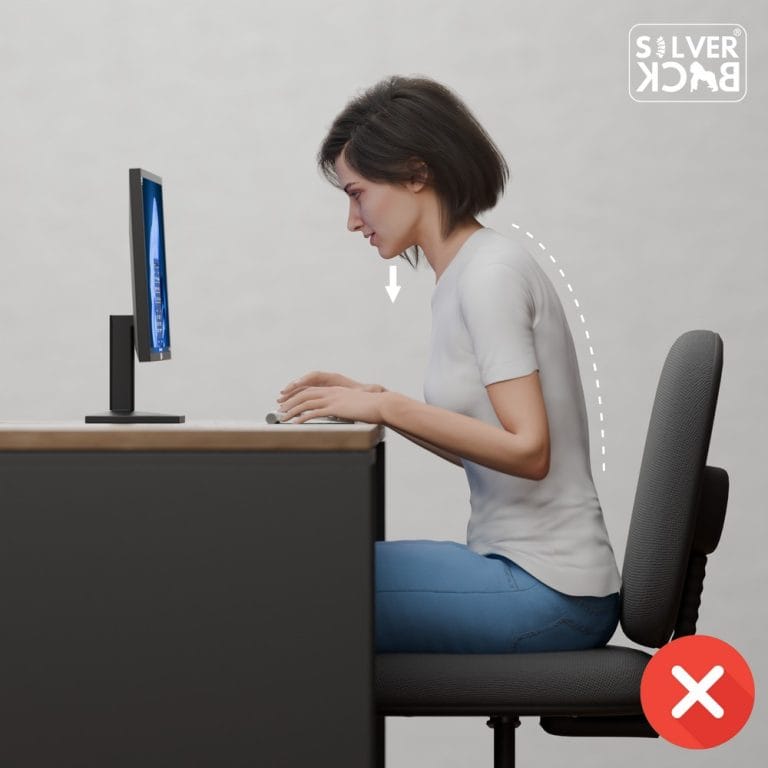
B. Ergonomic Office:
If you work at a desk, make sure that the environment is ergonomically structured to promote appropriate posture. Your computer monitor should be placed at eye level, your chair should support a neutral spine, and you should use an orthopedic cushion to provide additional lower back support. An orthopedic cushion helps reduce pressure on your spine, aligns your hips, and promotes better posture, making long periods of sitting more comfortable and healthier
C. Physical Activity:
Regular workouts, particularly strength and flexibility routines, can greatly improve entire posture.
D. Yoga and Pilates:
These practices emphasise posture and can help you develop body awareness and symmetry.
Conclusion:
Learning how to stand up straight is a gradual process, but the rewards are significant. By following these steps, performing targeted exercises, and being mindful of your posture throughout the day, you can improve your posture and experience the health benefits of standing up straight. Start today, and make standing tall a natural part of your life.
Finally, correcting posture is a continuous process that demands awareness and continual effort. People can progressively improve their alignment and get the benefits of good posture by making tiny modifications to their everyday behaviours and integrating posture-friendly practices. This not only reduces pain, but also improves confidence and general quality of everyday life. Remember that good posture is a journey rather than an end point, and every small step contributes to a healthier, happier you.
remember that changing your posture requires time and practice. Be conscious of how you stand and sit during the day. Regularly examine your posture and make any necessary modifications. Standing up straight will eventually become second nature.
FAQs:
- 1. What are the most important steps for ideal posture?
To enhance your posture, follow these tips. Sit erect, shoulders relaxed but not slouched, knees level, and utilise your chair to support your spine. Keeping an appropriate screen viewing angle can help prevent cyber neck. Stand up straight, perform regular physical activity, and include stretching into your daily activities.
- 2. How can I keep a straight posture when standing?
To stand up straight, maintain your head straight and your chin pushed in, with your ears directly above the centre of your shoulders. Pull your shoulders back, knees straight, and tucked stomach in. Avoid extending your hips or buttocks outwards.
- 3. What are the most efficient posture correction methods?
Proper posture entails maintaining a straight back, balancing your ears, shoulders, and hips, relaxing your shoulders, spreading your weight evenly on each of your feet, and keeping your knees straight but not locked.
- 4. What workouts will allow you to stand up straight?
Concentrate on workouts that will extend your chest and strengthen your back. Stretching can help release tight chest muscles and open up the chest. Strengthening the upper back muscles can also help correct posture by increasing their activity.
- 3)https://www.carepatron.com/templates/gaenslen-tests
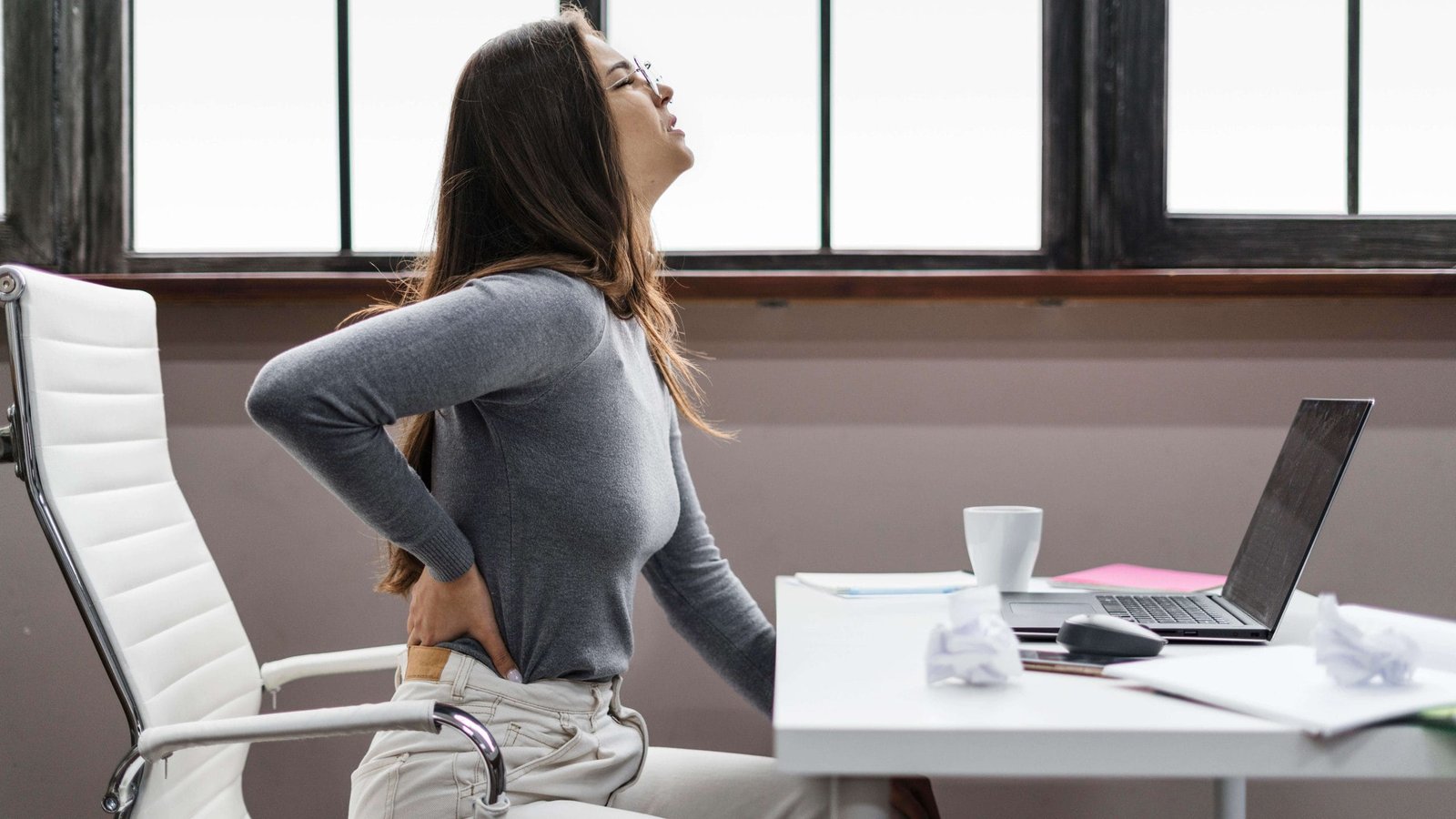

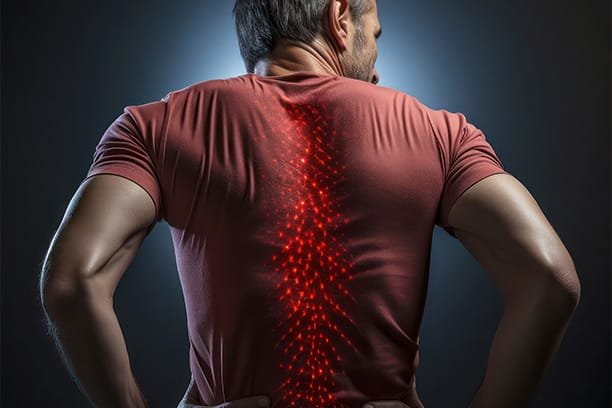

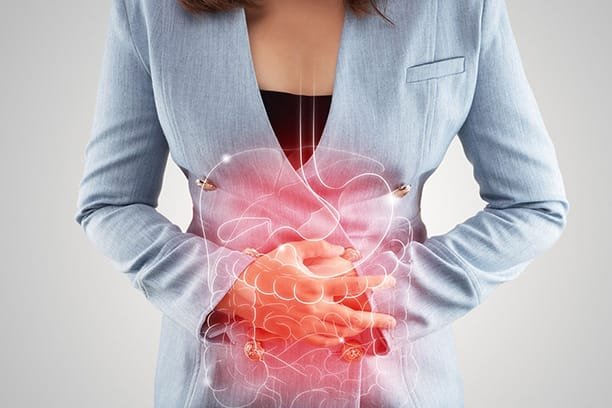
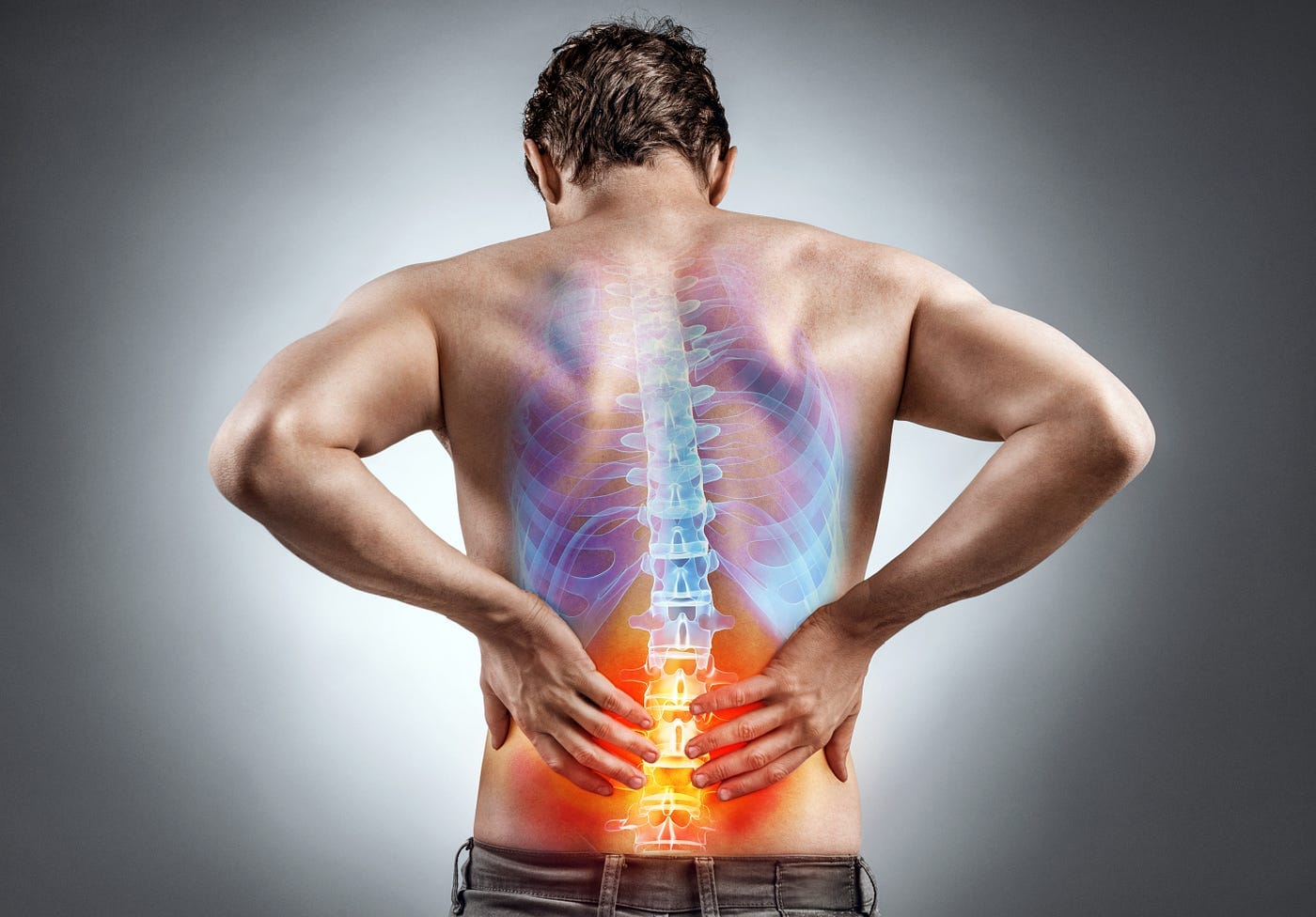










 Lower back pain is a common issue that affects many women worldwide. It can be debilitating and significantly impact daily activities. , we will explore the various factors that contribute to lower back pain in females, providing valuable insights into prevention and treatment.
Lower back pain is a common issue that affects many women worldwide. It can be debilitating and significantly impact daily activities. , we will explore the various factors that contribute to lower back pain in females, providing valuable insights into prevention and treatment.
 Structural issues such as herniated discs, bulging discs, or degenerative disc disease can also contribute to lower back pain in females. These conditions can put pressure on the nerves in the spine, causing pain and discomfort.
Structural issues such as herniated discs, bulging discs, or degenerative disc disease can also contribute to lower back pain in females. These conditions can put pressure on the nerves in the spine, causing pain and discomfort. Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, can affect the lower back and lead to pain in women. The wearing down of cartilage in the joints can result in inflammation and discomfort.
Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, can affect the lower back and lead to pain in women. The wearing down of cartilage in the joints can result in inflammation and discomfort.
 Poor posture, whether when sitting, standing, or moving, can contribute to lower back pain in females. Maintaining good posture can help alleviate discomfort and prevent future issues.
Poor posture, whether when sitting, standing, or moving, can contribute to lower back pain in females. Maintaining good posture can help alleviate discomfort and prevent future issues. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise can weaken the muscles in the lower back, making them more susceptible to injury and pain.Regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles and reduce the risk of lower back pain.
A sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise can weaken the muscles in the lower back, making them more susceptible to injury and pain.Regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles and reduce the risk of lower back pain. Engaging in regular exercise, particularly strengthening and stretching exercises, can help prevent lower back pain in females. Exercises that target the core and lower back muscles can improve strength and flexibility.
Engaging in regular exercise, particularly strengthening and stretching exercises, can help prevent lower back pain in females. Exercises that target the core and lower back muscles can improve strength and flexibility.
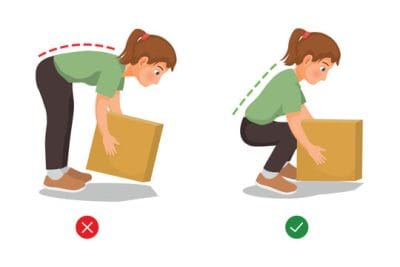 Using proper lifting techniques when lifting heavy objects can prevent strain and injury to the lower back. It is essential to bend the knees, keep the back straight, and lift with the legs to avoid putting unnecessary pressure on the spine.
Using proper lifting techniques when lifting heavy objects can prevent strain and injury to the lower back. It is essential to bend the knees, keep the back straight, and lift with the legs to avoid putting unnecessary pressure on the spine.